How Memory Works
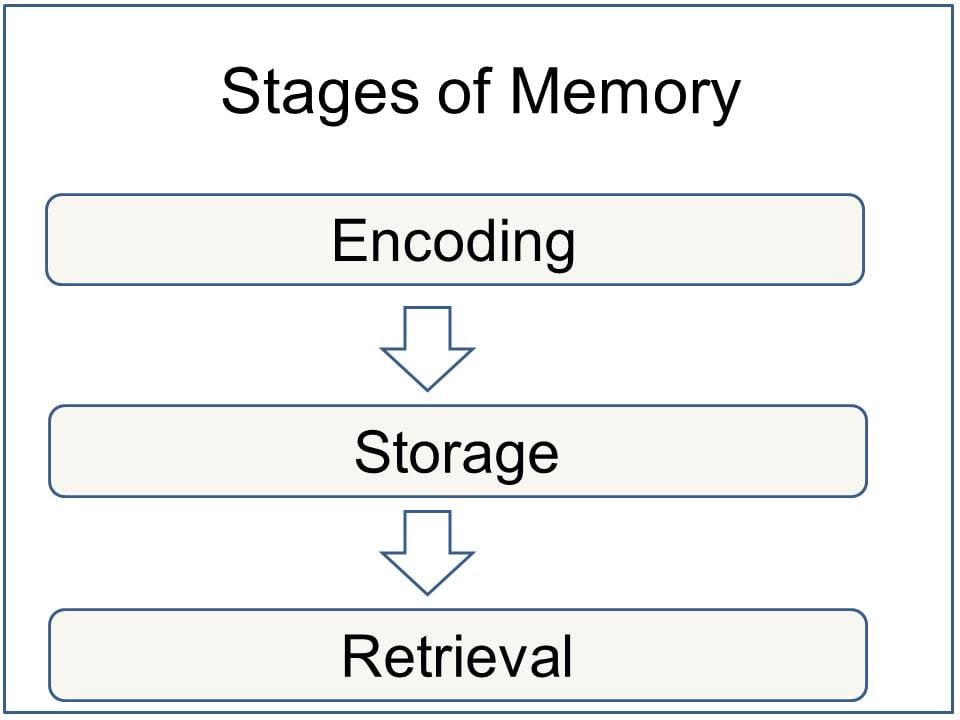
Memory works through three main processes:
- Encoding: The process of converting information into a form that can be stored in the brain.
- Storage: Maintaining information over time for later use.
- Retrieval: Accessing stored information when needed.
Cognitive theories explain how these processes involve different brain structures and mechanisms. For example, prospective memory allows us to remember to perform tasks in the future, while retrospective memory involves recalling past events.
Culture and individual differences also influence how we remember and what kinds of memories are prioritized.