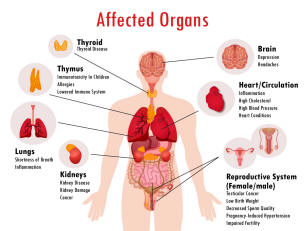
Impact on Health
Fast-food is a popular choice across the world due to its accessibility and convenience, yet it frequently has a harmful influence on health. According to Cadario, R. (2016). Regular fast-food consumption can result in several health problems because of the meals' high calorie density, high sugar and fat content, and inadequate nutritional value.
Obesity and Related Diseases
There is a clear correlation between the frequency of fast-food intake and the spread of obesity. Abu Elnasr, E. S., & Abdelaziz, A. S. (2022). States that “Studies often link eating out with obesity and the perceptions that FFOs often provide unhealthy food” (p. 2). Fast-food frequently has poor nutritional content and high calorie content, which can promote energy imbalances and weight gain. (Grossman et al., 2017, p. 65). This excess of calories, frequently combined with a stable lifestyle, raises the risk of obesity markedly, and obesity is a sign to other serious health issues including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and several cancers.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Fast-food frequently lacks vital elements that are necessary for sustaining general health, such fibre, vitamins, and minerals. Abu Elnasr, E. S., & Abdelaziz, A. S. (2022). Frequent ingestion of such meals can result in nutritional deficits, which can impact the immune system and long-term cognitive performance, among other things. For example, the deficiency of sufficient dietary fibre in several fast-food alternatives has been associated with an increased risk of developing heart disease and gastrointestinal issues.
Mental Health Effects
Recent studies also point to a possible connection between eating
fast-food and a number of mental health issues, such as a higher
chance of developing depression. Fast-food's high sugar content can
cause blood glucose levels to fluctuate, which can affect mood and
energy stability and perhaps exacerbate mental health issues
including anxiety and depression.
(Douglas, 2007).
Top_of_Page