Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication
Stay Secured with Strong passwords and 2FA
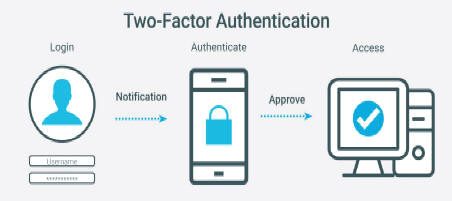
Strong passwords and two-factor authentication (2FA) are vital for online security. While passwords are the first line of defense, they can be easily compromised if not strong enough. Complex passwords, combining letters, numbers, and symbols, greatly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. However, passwords alone are not enough. 2FA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring a second verification step, such as a code sent to a mobile device. This can prevent the majority of cyberattacks.
In addition to one-time passwords, modern 2FA includes biometric options like fingerprint or facial recognition, security keys, and authentication apps such as Google Authenticator. Some organizations use adaptive authentication, which considers factors like device type and location to assess the security of a login attempt.
Despite its effectiveness, many users do not enable 2FA due to
convenience concerns and lack of awareness. Encouraging 2FA adoption
through education and policy enforcement is key to enhancing online
security.
| Topic | Details |
| Importance | Strong passwords and 2FA are essential for protecting online accounts from unauthorized access. |
| Password Requirements | Use complex passwords with a combination of letter, numbers, and symbols. |
| 2FA Overview | 2FA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring a second verification step( e.g, a one-time code). |
| Types of 2FA |
|
| Adaptive Authentication | Login attempts are evaluated based on factors like device type, location, and time. Additional verification is required if suspicious activity is detected. |
| Challenges to Adoption | Low adoption rates due to
convenience concerns Lack of user awareness |
| Solutions for Widespread Use |
|