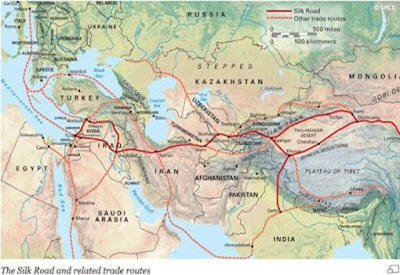
Routs And Geography
Even before airplanes, ships, or highways existed, people across Asia, the Middle East, and Europe were connected through trade, and one of the greatest networks that made this possible was the Silk Road. This was not a single road but a network of land and sea routes linking China with the Middle East, Central Asia, and Europe (Torr, 2018). The routes passed through deserts like the Taklamakan and Gobi, mountain ranges such as the Tian Shan, and valleys with oasis towns that provided water and shelter. Merchants followed paths along river valleys, mountain passes, and across the Indian Ocean, connecting China to India, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East. Despite harsh weather, the geography also offered safe resting spots and opportunities for cultures to meet and exchange goods like silk, glass, and spices, as well as ideas, art, religion, and technology (Torr, 2018).