Causes and diagnosis for Dyslexia
Dyslexia, a reading disorder, has various underlying causes. One significant factor is impaired visual processing, particularly in recognizing multiple letters simultaneously. This difficulty is like a condition called simultaneous agnosia, where individuals struggle to perceive multiple objects at once. Dyslexic readers may also experience challenges due to the crowding effect, where surrounding letters interfere with recognition. (Werth, 2023)
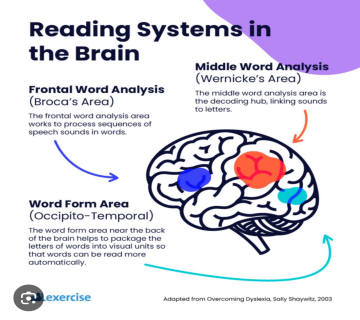
However, dyslexia are not solely visual. Phonological awareness, the ability to associate sounds with letters, is often implicated. But recent findings suggest that dyslexia are not exclusively caused by a deficit in this area. Instead, it's more complex, involving difficulties in controlling eye movements during reading. Dyslexic individuals may make irregular eye movements, impacting their reading abilities (Werth, 2023).
Diagnosing and managing dyslexia involves a comprehensive approach that considers various cognitive and neurological factors. Key aspects include:
- Assessing reading skills, phonological awareness, and visual processing abilities.
- Using functional MRI studies to identify differences in brain activation patterns between dyslexic and typical readers, especially in visual and phonological processing areas (Werth, 2023).
- Implementing training programs focused on phonological awareness, rapid naming, and reading skills, which have shown positive effects on reading abilities.
- Understanding the neural basis of dyslexia to inform targeted interventions that address underlying difficulties and improve reading outcomes (Werth, 2023).