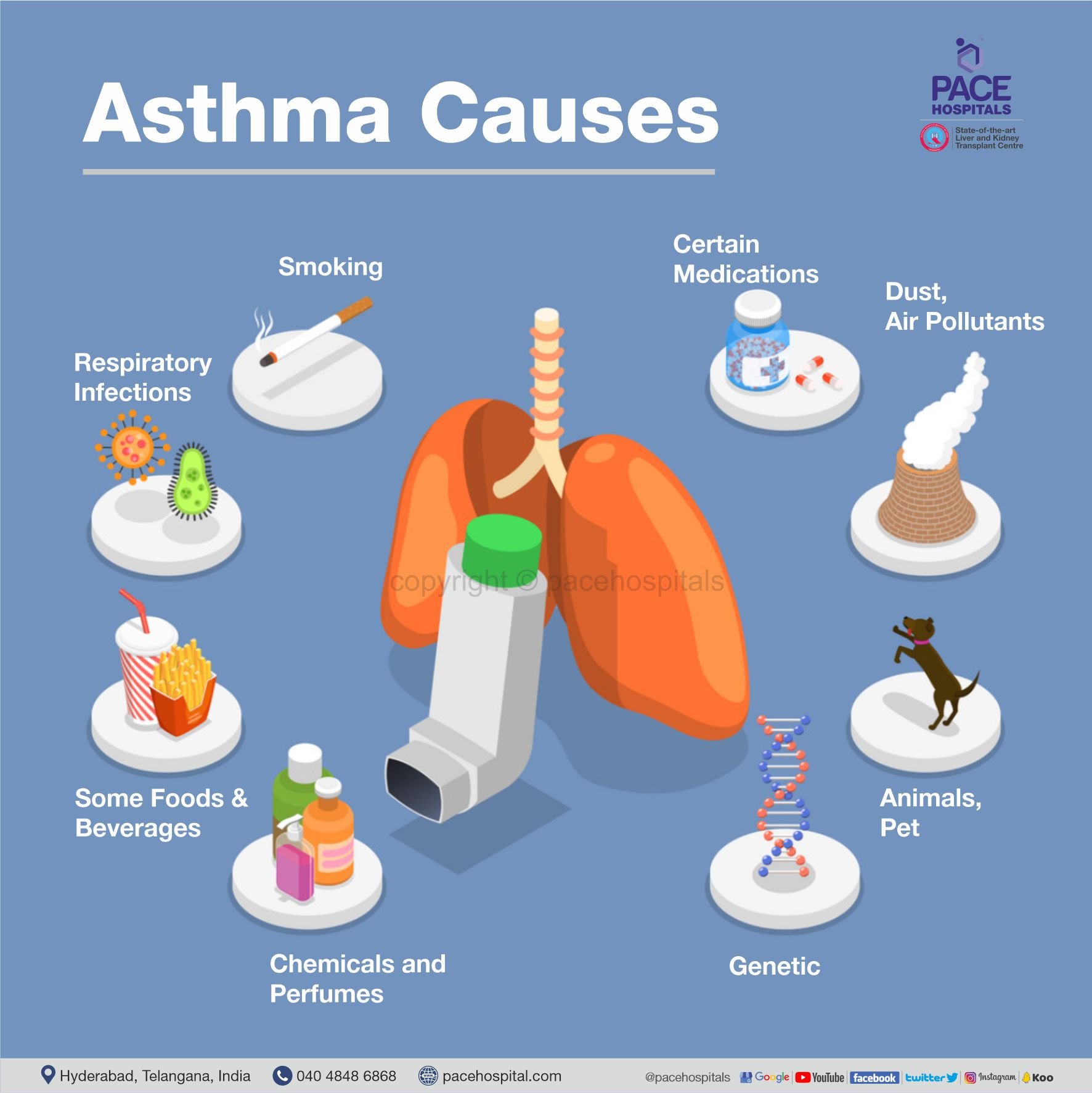
Causes of Asthma
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in asthma development. Family history of asthma or other allergic conditions increases the likelihood of developing asthma. Specific gene mutations, such as those involved in immune system regulation, may also contribute to the disease.
Environmental Factors
Environmental exposures, including allergens (e.g., pollen, dust mites, mold), air pollution, and respiratory infections, can trigger asthma symptoms. Exposure to tobacco smoke, chemicals, and strong odors also increases the risk of asthma development.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices, such as diet, physical activity, and exposure to stress, can influence asthma symptoms. Poor air quality and sedentary behavior may worsen the condition, while a healthy diet and regular exercise may help manage it.
Other Triggers
Triggers like cold air, strong emotions, exercise, and certain medications can exacerbate asthma symptoms. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is essential for effective asthma management.