Management Strategies for Asthma
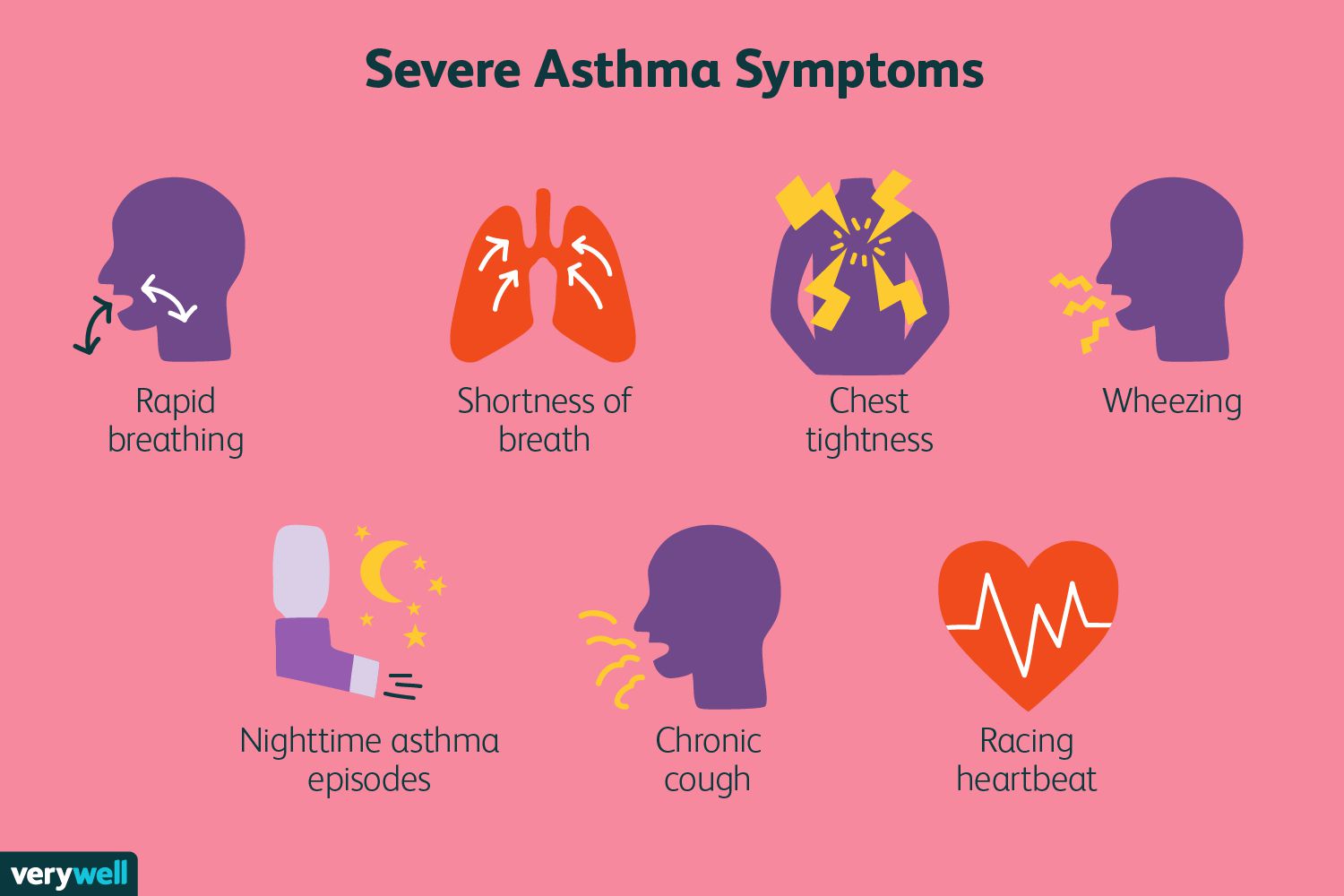
Asthma Overview
Asthma involves chronic airway inflammation, bronchoconstriction, and airway hyperresponsiveness. Immune cells, such as eosinophils, mast cells, and T-helper cells, release mediators like histamine and cytokines, leading to airway narrowing and mucus overproduction.
Key Features of Asthma
Inflammation and Swelling
Inflammation and swelling in the bronchial walls cause difficulty breathing, with attacks triggered by an exaggerated immune response.
Bronchoconstriction
Bronchoconstriction occurs when smooth muscles contract, reducing airflow. This is worsened by excess mucus production, which thickens the airway lining.
Airway Remodelling
Chronic inflammation leads to airway remodelling, characterized by thickened walls and increased mucus, resulting in persistent airflow obstruction and potential resistance to treatment.
Recent Research
Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Oxidative stress contributes to asthma by damaging epithelial cells and intensifying inflammation. Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory diets may reduce these effects and improve symptoms.
Implications for Management
Effective asthma management is crucial to prevent complications and improve lung function, ultimately enhancing quality of life for patients.