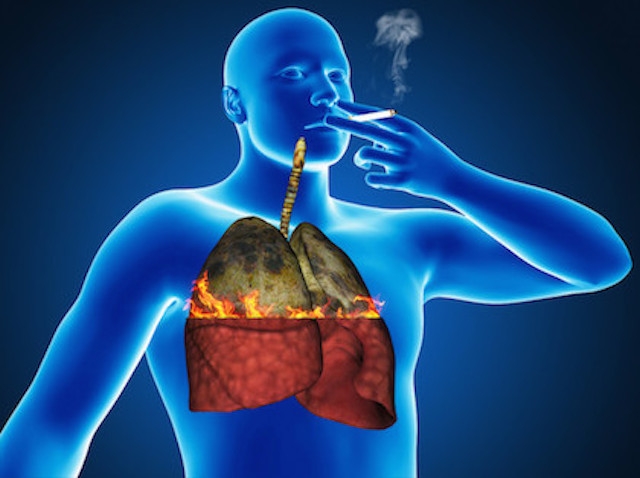
How Smoking Affects Health
Smoking is one of the leading causes of serious health problems. It damages the lungs, heart, and blood vessels, leading to diseases like lung cancer, heart attacks, and breathing problems such as asthma and bronchitis (Hajar, 2018). For example, many long-time smokers develop a persistent cough, often called a “smoker’s cough,” which is a sign of lung damage (Joseph et al., 2018). Over time, smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight infections (Carter et al., 2015). Additionally, smoking has been linked to an increased risk of death, including cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers (Campbell et al., 2008).
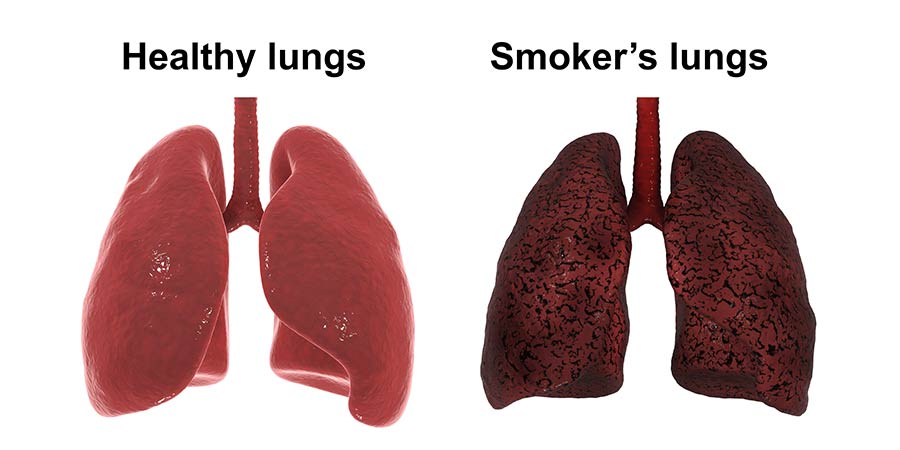 Second-hand
smoke is also a major concern. People who live with smokers,
especially children, are more likely to suffer from breathing
problems. For instance, a child who grows up in a home where people
smoke may develop asthma or frequent colds. Pregnant women exposed
to cigarette smoke are at risk of giving birth to babies with low
birth weight or other health complications. This shows that smoking
not only affects the person who smokes but also puts their loved
ones in danger (Riedel et al., 2014).
Second-hand
smoke is also a major concern. People who live with smokers,
especially children, are more likely to suffer from breathing
problems. For instance, a child who grows up in a home where people
smoke may develop asthma or frequent colds. Pregnant women exposed
to cigarette smoke are at risk of giving birth to babies with low
birth weight or other health complications. This shows that smoking
not only affects the person who smokes but also puts their loved
ones in danger (Riedel et al., 2014).