Technologies and Impact of Recycling
The lifetime of a product plays an important role in waste management and recovering materials for future technologies that are vital for sustainability. These include replacing non-renewable sources like gas with electric vehicles for transportation and wind turbines for continuous electricity.
-
Electric Vehicle Battery Systems
Rosenberg conducted a combined LCA and MFA to evaluate the environmental benefits of hydrometallurgical and direct recycling for EV battery systems. Both recycling methods positively impact the ecological footprint compared to using new materials to create new batteries. High-standard hydrometallurgical recycling offers advantages through graphite harvesting for battery-grade quality, saving approximately 3.8% in GHG emissions. In contrast, direct recycling may contribute to a 2.1% increase in GWP by burning graphite during copper recycling.
-
Wind Turbines
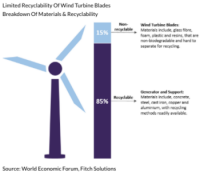
The key recycling methods for wind turbine technology include
mechanical recycling, pyrolysis, and chemical treatment. These processes
recover valuable materials from end-of-life wind turbine blades. The
current market status shows that many companies are working on recycling
wind turbine parts, but these methods suffer from high costs and a lack
of market for recyclates.
For example, companies like Damacq Recycling International in the
Netherlands, Eco-Wolf in the USA, ELG Carbon Fiber Ltd. in the UK, and
Karborek IT in Italy are working towards recycling wind turbine
components. More research and development are essential to improve these
methods and make them more economically viable and environmentally
friendly.
The environmental impact of recycling technologies varies based on the
method used. Advanced hydrometallurgical recycling emits fewer GHG
emissions, while direct recycling may have negative effects if not
managed properly.
| Recycling Technologies Overview | |||
| Recycling Method | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Pyrolysis | Recover fibers from CFRPS and GFRPS | Produces valuable by-products like oil alternatives | Hazardous and costly; requires char removal after processing |
| Mechanical Recycling | Crushes FRPS for reuse in new production | Cost- efficient; supports high throughput rates | Physical integrity of fibers disrupted; leads to property loss |
| Chemical Treatment | Produces high-quality fibers | High mechanical strength; effective for fiber recovery | Solvent use can impact efficiency; supercritical solvolysis is toxic |
| Fluidized- Bed Processing | Recovers fibers at high quality | Lower costs; effective for composite materials | Low economic viability; less environmentally friendly due to pollutants |
Impact of Recycling
Recycling has both advantages and disadvantages. Companies using
advanced recycling technologies reduce their carbon footprint and
minimize the need for raw materials, preserving natural resources. For
example, Rosenberg demonstrated that hydrometallurgical and direct
recycling of EV battery systems could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by
up to 4.55 kg CO2e/kg battery for NMC111 and NMC811 cathode materials.
Economic benefits include cost savings from reduced raw material
consumption and environmental benefits, such as reduced pollution.
Additionally, recycling promotes safe practices for sustainability,
providing a model for other industries.
Landfills occupy non-inhabitable spaces, whereas effective waste
management through recycling can significantly reduce the need for
landfills, allowing more ecological industries like wind energy and
hydroelectricity to utilize that space. Landfilling requires substantial
space and does not recover the energy from composites, while
incineration produces harmful gases.
Advanced recycling technologies can benefit industries through cost
savings and contribute to a global economic and ecological footprint.
The combination of LCA and MFA, as demonstrated by Rosenberg, highlights
the environmental benefits of recycling and identifies areas for future
improvement.
