Types of Plastic Surgery
Cosmetic surgery and reconstructive surgery are the two primary areas into which plastic surgery falls. Although each category has a unique function, they frequently apply related techniques in multiple ways.
Cosmetic Surgery
The main goal of cosmetic surgery is to improve a patient's look in order to satisfy their aesthetic preferences. Common examples of cosmetic surgery procedures include liposuction, rhinoplasty, and facelifts (Canadian Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 2015). Due in great part to media representations of idealized beauty standards, breast augmentation has become increasingly popular in recent decades, making it one of the most common cosmetic procedures performed globally (Canadian Society for Surgery of the Hand, 2015). Cosmetic surgery can improve a person's body image and sense of self, but it can also have harmful impacts, especially if it is motivated by social pressure.
Modern community standards of beauty are becoming more closely linked to cosmetic surgery, since celebrities, the media, and social media frequently create trends that affect people's decisions to have surgery (Hodges, 2008). For example, media representations of Western beauty standards have contributed to the growing popularity of cosmetic surgery in Asia, which has raised demand for jaw reshaping and double eyelid procedures.
But according to certain psychologists and ethicists, bodily dysmorphia and unrealistic expectations of beauty are issues brought on by the pressure to fit into a single ideal of beauty (Canadian Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 2015). Whether society should continue to focus limited and frequently unachievable norms or embrace a variety of body types and beauty standards is a topic of continuous discussion.
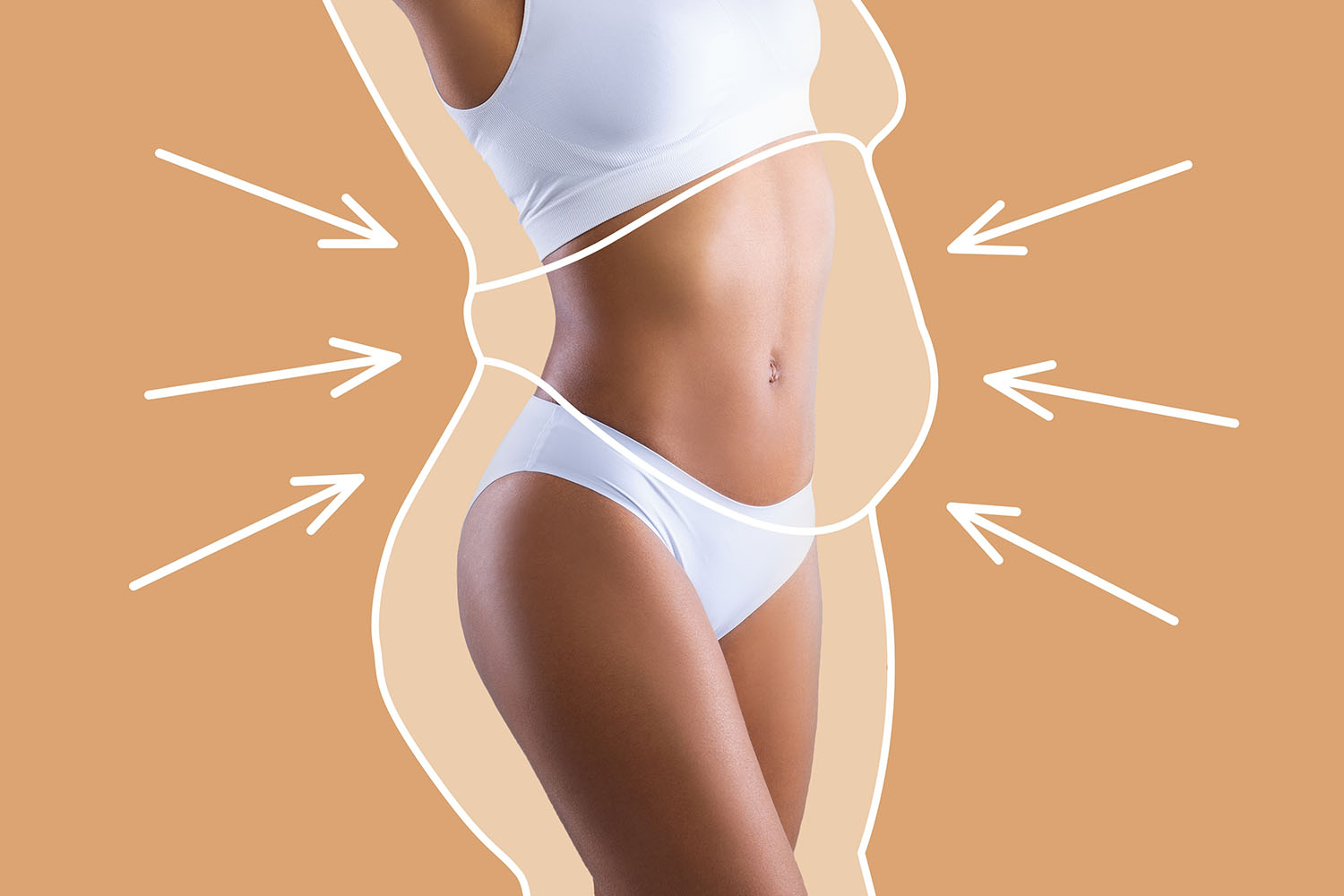

Liposuction
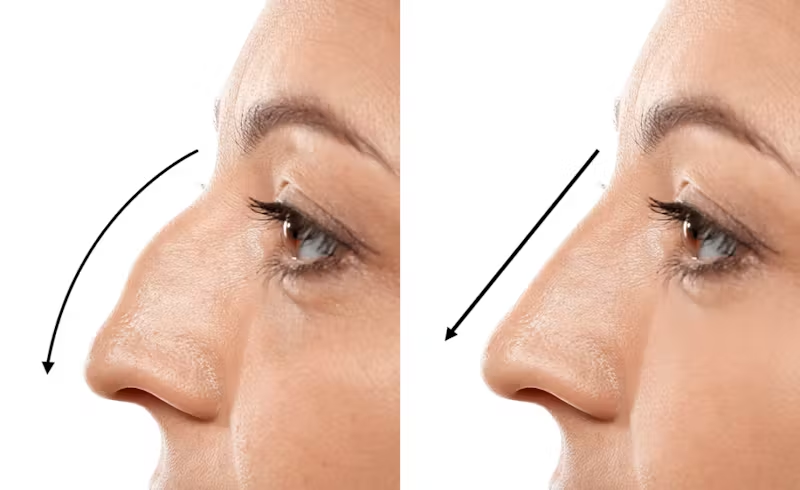
Rhinoplasty
Reconstructive Surgery
In contrast, the main goal of reconstructive surgery is to restore appearance and function following damage, birth defects, or illnesses like cancer. Examples of reconstructive operations include burn treatments, cleft lip and palate restoration, and post-mastectomy breast reconstruction (Jones & Janis, 2006). By helping patients regain physical function and a sense of normalcy following operations or accidents, reconstructive surgery is essential to improve their quality of life.
Surgeons may now undertake more intricate restorations, like replanting severed limbs and transferring healthy tissue to restore damaged areas, thanks to microvascular surgery, a significant advancement in the discipline (Bullocks, 2017). This method has proved crucial in improving the results of trauma procedures, when the objective is to restore functionality in addition to fixing physical damage.
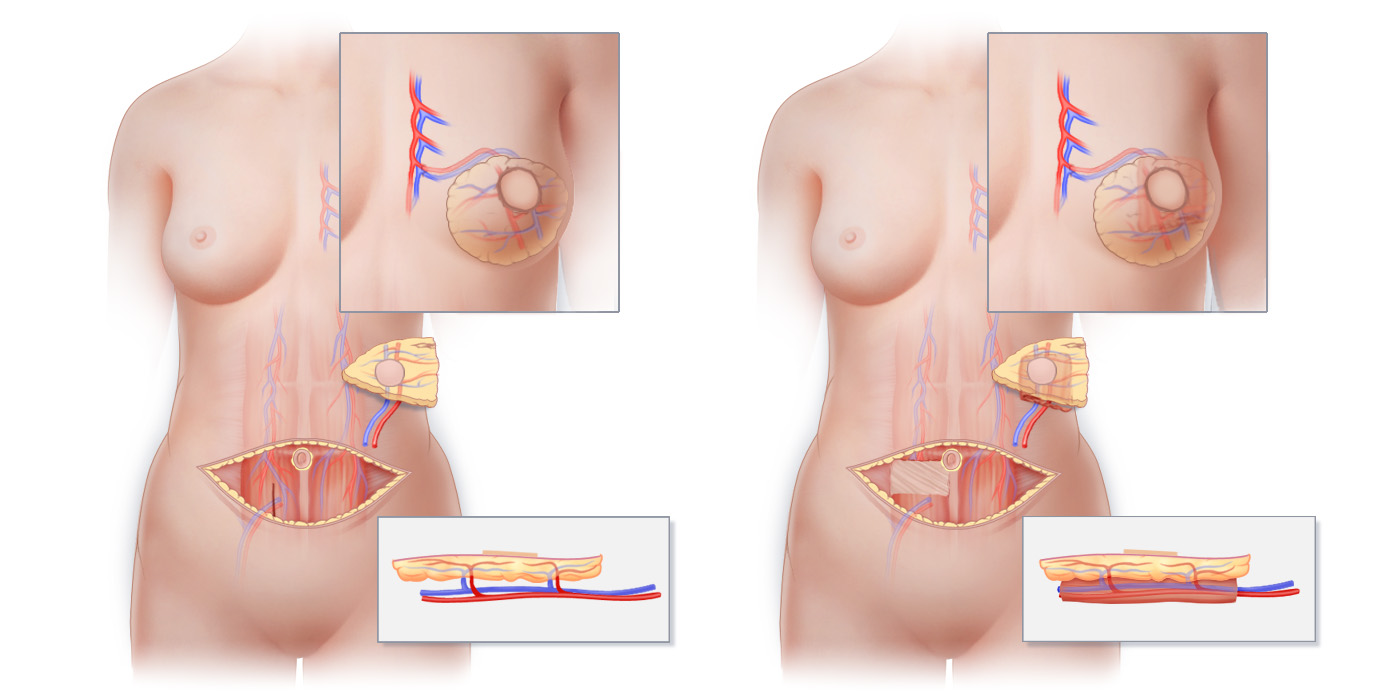
Post mastectomy breast restoration