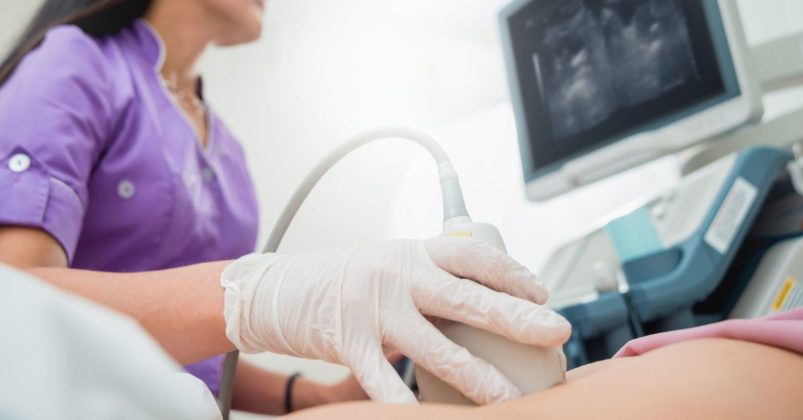
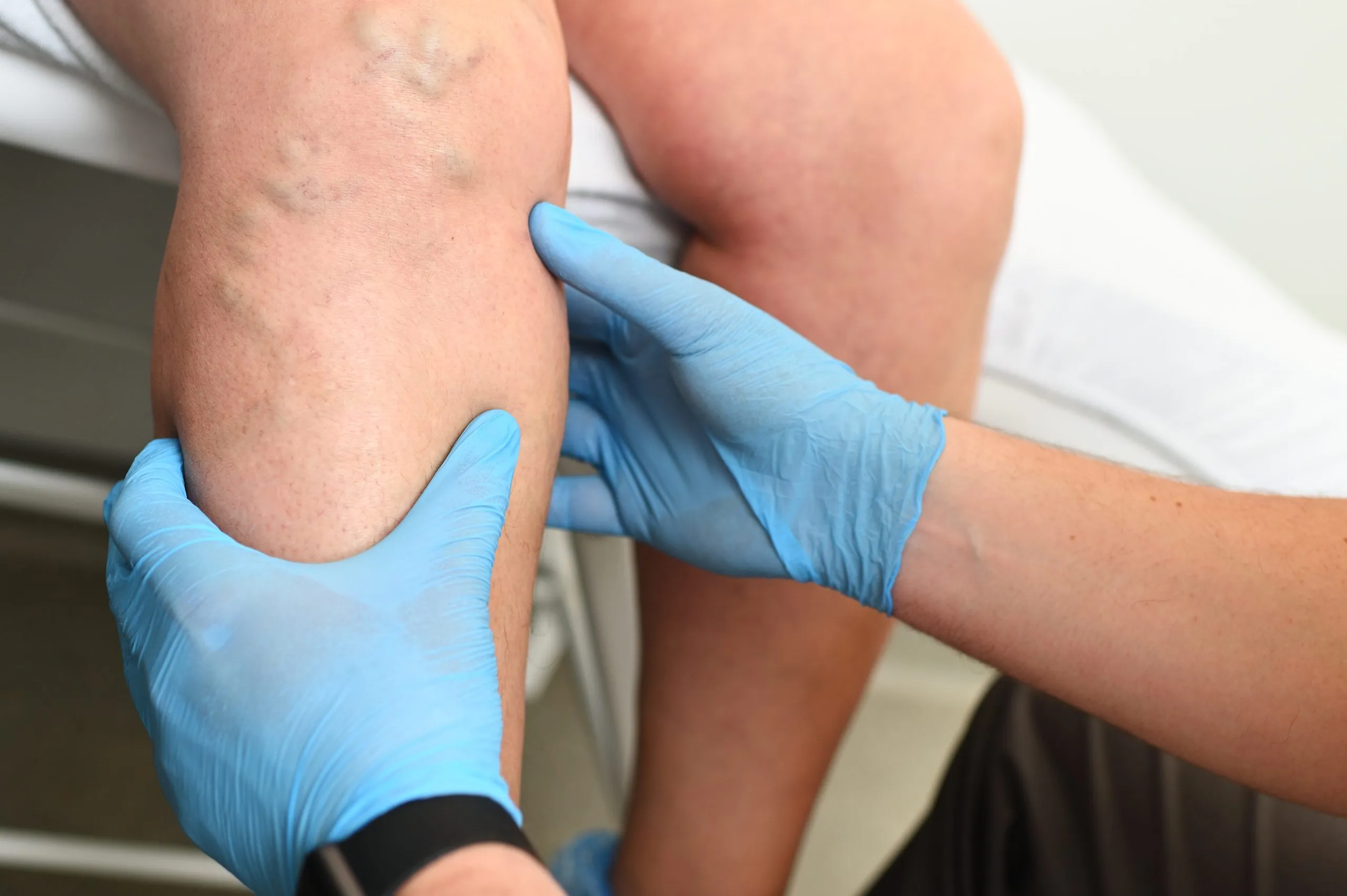
Diagnosis
Identifying lower limb deep vein thrombosis from the history and physical examination might be difficult. Both DVT and PE can cause life threatening diseases if left untreated (Judd, 2014). While some people exhibit calf muscle soreness and edema, others show no symptoms at all. The tissues of the muscles become continually inflated due to an obstruction in the vein, leading to edema. The diagnosis may be confused with other conditions that cause aches and pains in the lower limbs such as a muscle tear, muscle cramps, a ruptured Baker's cyst, cellulitis, and postphle-bitic syndrome (Khan, 2006)
Diagnostic Methods:
As per Encyclopedia of Heart, three methods can be used to detect the presence of clots in the veins named as d-Dimer, Ultrasonography, Venography.
In D-Dimer test, when testing for potential venous thromboembolism, measuring the breakdown products of cross-link fibrin (D-dimer) in the bloodstream is a highly sensitive but generic test. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent test (ELISA) is used to assess D-dimer. However, in over 90% of cases, a negative test result gives confidence that a dangerous event like a pulmonary embolism is not present. Clinical research suggests that if a patient has a negative D-dimer test and is considered clinically unlikely to have deep vein thrombosis, deep venous thrombosis can be ruled out.
Secondly, when patients have signs and symptoms, pressure ultrasonography is performed by skilled experts may correctly detect above-the-knee thrombosis. It's possible that a tiny clot or an incomplete blockage goes undetected. In individuals who are symptomatic, the test is sensitive and specific; however, in patients who are asymptomatic, the sensitivity is only 59%. Furthermore, the much-praised test is unable to clearly show the deep veins in the leg or pelvis.
Last but not the least, Venography is yet another technique used to diagnose DVT and other similar concerns. Venography is usually recommended when all other tests such as d-dimer, scans, ultrasonography have not given sure and certain results.
Venography is the preferred examination for patients whose diagnosis from D-dimer, ultrasonography, and clinical evaluation by a doctor is uncertain. Algorithms do not cover every possible case, but around 12 hours before operation is when this test is performed. This tactic has changed recently. Hull found that LMWH proved far more effective than traditional oral anticoagulants in a study conducted about six hours after surgery, without any increasing the risk of bleeding. This method lowered the risk of proximal (above-the-knee) deep vein thrombosis by 72% and the risk of total deep vein thrombosis by 50% (p < 0.001). According to other investigations, starting deep vein thrombosis prophylaxis soon after surgery has the greatest benefits.
CONTACT US
My Email Contact: Muskan Muskan - Send Email