Understanding the Sicence behind Climate Change
A closer look at the science behind climate reveals a complex web of
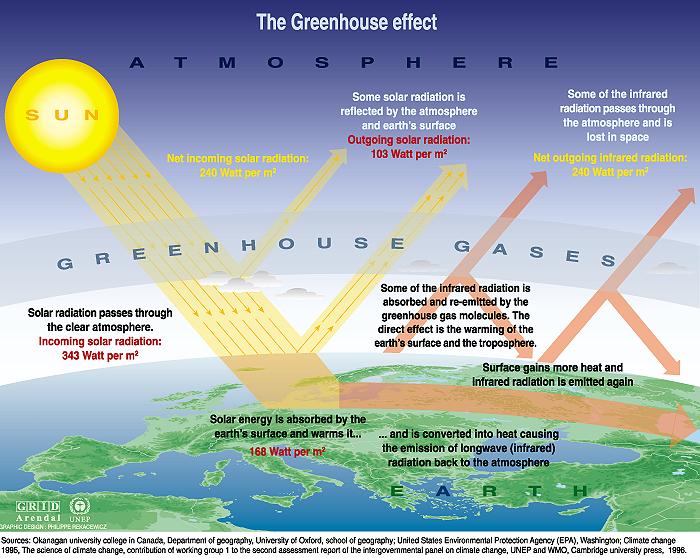
interrelated mechanisms that control the planet’s climate. The intricacy
of the greenhouse effect is highlighted by its subtleties and
interconnections with other Earth systems, even though it is a key
concept in the study of climate change. For example, feedback loops- in
which the impact of climate change intensify or lesson those of its own
drivers-are essential in determining how global warming will develop.
Warming trends are made worse by positive feedback loops, such as the
melting of the polar ice caps, which reduce reflection (albedo) and
increase solar radiation absorption In contrast, carbon dioxide uptake
by terrestrial and oceanic sinks, or negative feedback loops, offer a
naturally occurring way to control atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
Additionally, advances in climate modelling have allowed scientists
to forecast future climate scenarios with greater accuracy, providing
crucial knowledge about potential repercussion and assisting in
decision-making. By merging information from many sources, including
paleoclimate reconstructions, satellite observations, and ground-based
measurements, researchers aim to increase our knowledge of climate
dynamics and accuracy of climate projections.